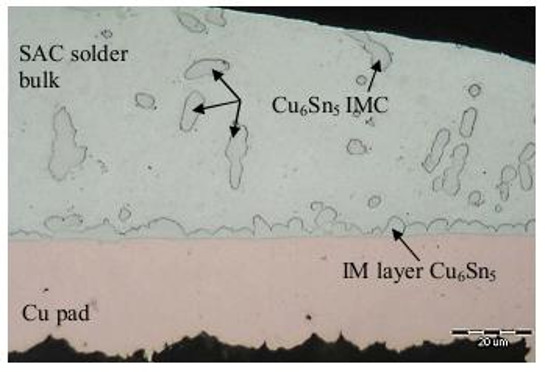
PCB Finishes
The finish of a board is the interface between the board and the components. It provides a more solderable surface than copper, reduces oxidation of the exposed pads, and lengthens the shelf life https://royal-ems.hd-staging.net/wp-admin/edit.php?post_type=pageof the boards.
Download AllMethods for Finish Application

Dip Coating
PCB is dipped into molten solder or other substance.

Electroless
Electroless is similar to Immersion but it is not dependent on the metal’s nobility (thicker than immersion).

Immersion
This method relies on the chemical reaction with a more noble dip metal (thinner than dip coating).

Electrolytic
This method uses charge to attract atoms of plating material to the board (hard and thick layer).
Kinds of Finishes
Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG)
- Ideal for small SMD and BGA Devices
- Extermely flat / planar surface
- 12 month shelf life
Immersion Tin
- Has low friction coefficient
- Ideal for pressfit pins
- Highly susceptible to corrosion
- 2.5 – 3 months shelf life
Immersion Silver
- Highly resistant to corrosion
- Has high friction coefficient
- Not ideal for pressfit pins
- 2.5 – 3 months shelf life
Organic Solderability Preservation (OSP)
- Extremely thin and plane surface
- transparent finish makes it difficult to inspect
- 2.5 – 3 months shelf life
Hard Gold or Electrolytic Gold
- Commonly used for non-soldering needs
- Focused on copper protection
- Requires special design
Royal Circuits' Standard Finish Offerings
- HASL / HASL PB FREE
- White Tin
- Electroless Nickel / Palladium / Gold – ENEPIG
- Electroless Nickel / Immersion / Gold – ENIG
- Immersion Silver
- Entek Plus HT / OSP
Finishes are typically the final step of the manufacturing process. While finishes may not be as important as other design stages, it is still not something that should be treated lightly.
A proper finish, in conjunction with other design considerations, will certainly make boards of the highest quality at a lower wastage and rework level.